
For retailers, inventory is more than just a list of products: It’s also the mainstay of your retail operations, the source of your revenue, and the foundation of customer satisfaction.
Retail inventory management is therefore the key to managing inventory costs and movements effectively.
This article will help you understand how it works, why it’s so important, and which best-practice retail inventory management techniques can ensure efficient stock control.
What is retail inventory management?
Retail inventory management is the process of tracking and controlling the flow of retail inventory stock from your suppliers through to your customers. It involves forecasting, planning, ordering, and storing the optimal amount of inventory for each type of product you sell across all sales channels.
The main goal of retail inventory management is to optimise inventory levels and reduce costs while increasing sales and improving customer satisfaction.
Retail inventory management can be achieved through manual processes or with the help of retail software tools that automate and simplify tasks. Hardware such as barcode scanners and pallet jacks can also be implemented to aid in streamlining your inventory processes.
The importance of inventory management in retail
Effective retail inventory management is crucial for retailers because it helps increase profits, reduce costs, and improve customer service and satisfaction.
By using retail inventory management tools and methods, retailers can track product locations, quantities, sales patterns, profit margins, and reorder points. You can also avoid spoilage and obsolescence of products that expire or become outdated.
Retail inventory management helps you balance your investment in retail inventory with sales performance to gain greater efficiency and competitiveness.
How retail store inventory management works
The retail store inventory management process works by implementing processes and systems for efficiently tracking product quantity, location, and movement in the store and across different sales channels.
It aims to ensure that you have enough products to meet customer demand without having too much or too little inventory stock. When done well, retail inventory management will optimise inventory levels, reduce costs, increase retail sales, and improve customer satisfaction.
Here’s how the retail inventory management process works.
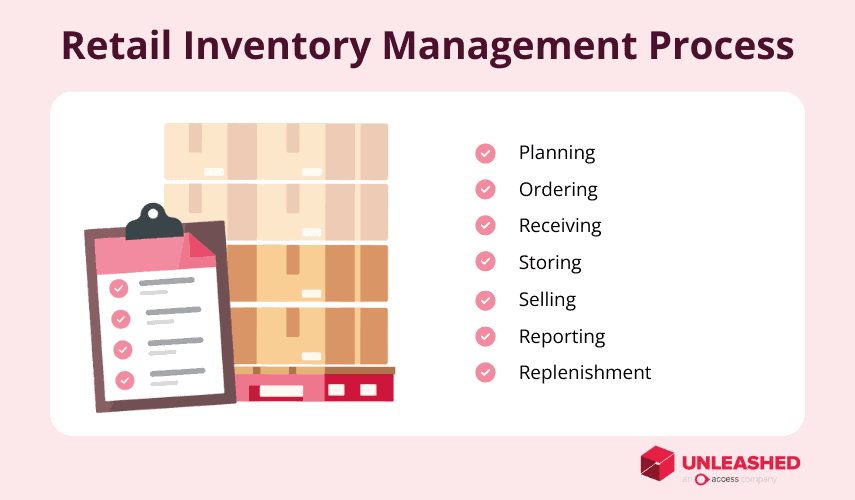
7 basic steps in retail inventory management
The 7 basic steps in retail inventory management are:
- Planning
- Ordering
- Receiving
- Storing
- Selling
- Reporting
- Replenishment
Let’s break these down.
1. Plan
Retail inventory management begins with planning the type and variety of products to buy (and their respective quantities). Inventory plans should be based on sales forecasts, market trends, and customer preferences.
To manage the inventory in your retail store, it’s important to have a strategy to help guide what and how much to buy. This requires an analysis of your sales data, seasonality, market demand, and customer feedback for different products.
By doing this, you can optimise the inventory levels in your retail operations to avoid overstocking or understocking and increase the profitability of your business.
2. Order
When you’ve developed your strategy and have your inventory plan in place, you need to order products from suppliers or manufacturers. Placing orders with suppliers should be based on your forecasted demand, current inventory levels, and supplier lead time.
Using tools like purchase orders, invoices, and receipts will help you to keep track of:
- Orders you’ve made to suppliers
- Orders you’ve received from customers
- Payments made to suppliers
- Goods delivered to their customers
3. Receive
Once your products arrive at your warehouse or retail store, they need to be checked and verified. This means inspecting the quality, quantity, and condition of the goods.
Check the accuracy of the receipted order by matching it with the purchase orders (before recording it in your inventory system and storing the goods in the warehouse or store).
Using inventory tools such as barcodes, scanners, and labels will help to ensure accuracy and accountability when receiving inventory.
4. Store
How you store your inventory will largely depend on the type of inventory you have.
Different types of products have different storage requirements. Retailers who hold perishable products or ones requiring temperature control, for example, will need to consider dry and cool storage options.
Dry storage is used for items that do not need refrigeration but may require ventilation, certain lighting, or humidity control and must be correctly stored and labelled. Cool storage is used for goods that need to be kept at low temperatures or in temperature-controlled environments, such as food and beverage, produce, and pharmaceutical items.
Some common methods of arranging inventory in both dry and cool storage areas include:
- Stacking: Placing items on top of each other, usually in their original packaging or containers.
- Shelving: Placing inventory on shelves or racks, labelled with the product name and relevant SKU data.
- Bins: Great for storing loose or bulk items. Bins should have tight-fitting lids and labels to prevent contamination and spoilage of perishable products.
Storing inventory properly will help you maintain product quality and safety, reduce waste and costs, and improve efficiency and productivity.
5. Sell
Retailers can sell products to customers through a variety of channels, such as in-store or via eCommerce, social media, and marketplace platforms.
By using tools like POS systems – and offering a choice of payment methods, and shipping options – your customers can shop when, where, and how they like. That means online and in-store, with tools to make their transactions easy and convenient and delivery options to suit their needs.
6. Report
Retail inventory management software enables you to monitor and analyse your inventory performance using metrics such as sales, turnover, margins, and shrinkage.
With software tools and dashboards, you can generate reports and visuals to show your sales volume, turnover rate, profit margins, and even the shrinkage rate of different products.
Accurate inventory reports not only help you to identify inventory patterns and trends – they can also simplify end-of-year financial reporting obligations.
7. Restock
It’s important to get your restocking and reordering right so that you avoid overstocking or understocking your retail inventory.
To replenish your stock and safeguard against running out of inventory, implement measures such as reorder points and par levels. These notify you when the stock reaches a predetermined minimum, helping you avoid running out of products when levels are low or when there is a spike in demand.

Retail inventory management best practices
Now let’s explore some of the best practices for retail inventory management.
1. Establish KPIs
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are designed to measure performance over specified periods so you can meet certain goals.
By establishing inventory KPIs, you’ll have a clear understanding of any weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annual milestones you’d like to meet. KPIs will also provide you with smart data that helps you to make smart business decisions.
Some of the KPIs you need to know include inventory turnover ratio, inventory-to-sales ratio and order fill rates and cycle times. These metrics can help you evaluate your inventory performance and identify areas for improvement.
2. Use ABC analysis
The ABC analysis method is where you arrange your inventory in order of the most important items to the least important items.
The A items are considered the highest priority stock and require frequent reordering, while the B items are valuable but are medium priority and ordered once a month. The C items are low-priority stock items that don’t need to be reordered very often because they are generally held in high volumes.
Using ABC analysis to organise your inventory means you can optimise your storage space and streamline fulfilment.
3. Create a stock receipt strategy
To ensure the accuracy of your stock receipts, check, and record goods as they are received.
Unpack entire shipments completely and check products for any errors, shortages, or damage. Count inward goods against purchase orders, follow up with suppliers when mistakes are identified, and update stock counts in your inventory management system.
- Learn more: How to Improve Receiving Efficiency
4. Invest in retail inventory management software
While it’s possible to manage your inventory manually, this can be time-consuming and risky.
Inventory management software and POS systems automate many of your processes and can help you understand how your inventory is moving. These tools can also make it easier to expand to other brick-and-mortar locations or eCommerce platforms.
Implementing retail inventory management software leads to fewer errors, improved efficiency, and increased productivity.
5. Build strong supplier relationships
By building strong relationships with suppliers, you may be able to negotiate better terms and prices, lock in discounts or incentives, and seek feedback. This helps to reduce the risk of delays and quality issues and simplify your inventory management.
Maintain good communication and collaboration with your suppliers to ensure timely and quality delivery of your inventory.
6. Calculate optimal minimum stock levels
The minimum stock threshold refers to the least amount of inventory you always need in your warehouse. Implementing minimum stock levels allows you to meet demand and reduce the risk of long lead times.
To calculate your minimum stock threshold limits or PAR levels use this formula:
Reorder Point – (Normal Consumption × Normal Delivery Time) = Minimum Stock Level
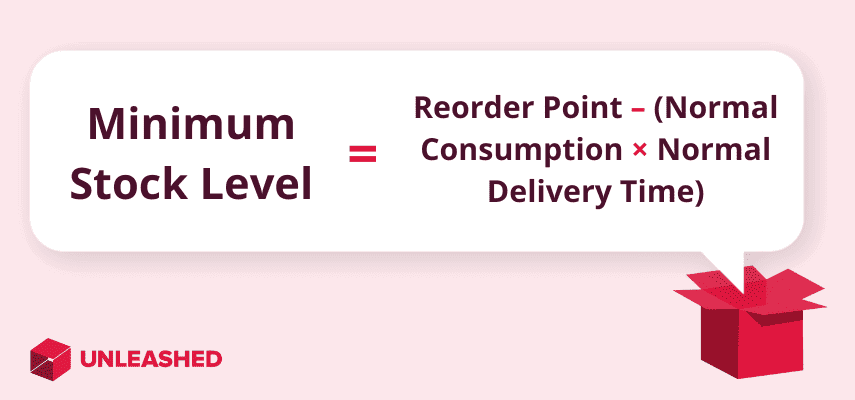
Knowing your optimal minimum stock levels means you’ll be equipped to always have enough stock on hand to deal with an unexpected spike in sales.
7. Implementing automation
Automation is one of the most productive ways to improve retail inventory efficiencies. It provides real-time visibility into your retail operations.
You can use tools like barcode scanners, RFID tags, and inventory management software to automate tasks such as ordering, receiving, and transferring inventory.
Automation can save you time, reduce human error, and increase your retail stock efficiency.
8. Manage residual inventory
Residual inventory is leftover inventory at the end of one season. For example, if you’re a clothing retailer, you may have leftover hats and scarves at the end of the winter season.
To manage and reduce residual inventory, create seasonal codes with style numbers so that when you enter the items into your inventory management system, it’s easier to analyse sales and seasonal inventory.
This will help you better prepare for future seasons.
9. Regularly audit inventory
Systematically auditing your inventory is a crucial process that helps you keep track of your stock levels, identify discrepancies, and optimise your retail activities.
You should perform physical counts of your inventory periodically to verify that your inventory records are accurate, your products are in good condition, and your customers are satisfied.
By conducting regular audits, you can also identify any issues like shrinkage, spoilage, or obsolescence.
Retail inventory management systems
Retail inventory management systems are methods, tools, and techniques that help retailers keep track of stock levels, sales, orders, and inventory costs.

Spreadsheet-based inventory management system for retail
Spreadsheets are a simple and low-cost way of managing inventory using a computer program like Microsoft Excel. A spreadsheet allows you to manually enter data such as product names, quantities, prices, and locations.
Excel spreadsheets can perform calculations and generate reports and charts based on the entered data.
However, the limitations of using spreadsheet-based inventory management include:
- Susceptibility to human errors
- The need for constant updates
- A lack of security and integration features
- Inability to perform complex tasks
For growing businesses with advanced inventory needs, a more automated system may be required.
Retail inventory management software
Retail inventory management software is a more advanced and automated way of managing inventory. It can be used to scan barcodes to capture product details, inventory levels, and sales data automatically.
Robust inventory software like Unleashed syncs data across multiple devices and locations, generates real-time reports and low-stock alerts, and can be integrated with your other software systems like accounting and eCommerce.
This video provides a short overview of how it works:
ERP software for retail inventory management
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive and integrated way of managing inventory along with other business functions using a centralised system.
ERP systems can coordinate data from various sources and departments, including inventory, sales, purchasing, finance, and human resources. An ERP system can also provide advanced analytics and insights, optimise your business processes and workflows, and support strategic decision-making.
However, ERP has some unique challenges. It can be complex and costly to implement and operate, requires significant organisational change and adaptation, and has security and scalability risks.
