
A barcode inventory system allows goods to be tracked along the supply chain and within a company’s storage facilities. It uses technology such as barcode scanners and barcode inventory software (like Unleashed - see demo) to improve the accuracy of your inventory management processes.
In this article we break down what a barcode system is, how it works, and how to set up a barcode system in a warehouse, a factory, or a small business. Let’s get right into it.
What is a barcode inventory system?
A barcode inventory system is a network of hardware and software consisting primarily of mobile computers, printers, handheld scanners, infrastructure, and supporting software. By automating the process of picking and counting inventory items, barcode inventory systems can help ensure goods are correctly picked and counted every time.
Inventory management and barcoding are highly compatible processes. Barcodes present a way of automating several otherwise-manual inventory control tasks to lift productivity and stock accuracy.
Barcode inventory systems are used in a multitude of industries and can be customised to suit specific business needs. However, there is no significant difference between barcodes used in a warehouse and those used in retail stores, distribution centres, or manufacturing firms.
What are barcodes?
Barcodes are unique numbers that associate several data points to a product, including information on who the supplier is, product dimensions, weight, and even variable data, such as the quantity of that product in stock.
There are over 100 different types of barcode symbols, typically one or two-dimensional.
A linear or one-dimensional barcode is the more commonly recognised type, characterised by parallel lines of varying widths and spacings. In contrast, two-dimensional barcodes use squares or rectangles and contain numerous small individual dots and geometric patterns similar to a QR code.
A barcode inventory system uses this array of symbols to track your inventory with greater speed and accuracy. Products are labelled with barcodes, scanned with a handheld mobile device, and synchronised with inventory management software in real time.
How does a barcode inventory system work?
A barcode inventory system works by encoding data into a series of vertical bars and spaces of varying widths. The bars and spaces – called barcodes – represent a sequence of numbers or characters that can be read by a barcode scanner.
A barcode inventory system assigns one of these barcodes to every one of your products. The scanner reads the barcode by shining a light on it and measuring the amount of light that is reflected. This information is then translated into data that can be used by the system.
Barcodes scanned at the retail point of sale (POS) need to support omnidirectional scanning. However, if your barcode is scanned at POS as well as in the warehouse, you will need to use a symbol that accommodates point-of-sale scanning but can be printed in a larger size to adapt to scanning in the distribution process.

Benefits of barcode inventory systems
Barcode inventory systems are popular tools for increasing business efficiency and productivity. They reduce human error, optimise data entry, and streamline processes – no more manual counting of all your widgets by hand.
5 helpful benefits of barcode inventory systems:
- Greater accuracy of inventory tracking and recording. With barcode inventory systems you reduce manual processes prone to human error, such as misreading numbers, skipping lines, incorrect input into your inventory system, or simply bad handwriting.
- Barcode scanning is more precise, reliable, and faster than manual data entry. When barcodes are read by scanners, the symbols are quickly and accurately translated into your inventory software system. Employees who use barcode systems work better than your employees who rely only on manual data entry.
- Barcode labels improve your data collection processes. Barcode inventory system label and scanning methods adapt to many applications across a range of industries to increase efficiency in several ways.
- Scanning systems streamline processes that help to eliminate preventable errors. In the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries, for example, barcode inventory systems will reduce medication errors when implemented correctly.
- Barcode inventory systems improve data analysis. Better data provides more accurate inventory information and real-time reporting. Notifications will alert you when inventory hits a certain threshold so you can reorder to meet production or sales demand.
As with other methods of supply chain automation, a barcode inventory system’s primary role is to enable businesses to get more done, in less time, with fewer costs to the business.
How to implement a barcode system for inventory
To implement a barcode system for inventory control, follow these steps:
- Obtain a GS1 Company Prefix. This allows you to create unique identification keys for various items which are used globally to identify everything in a supply chain.
- Assign identification numbers to your inventory items. Each item in your inventory will need a unique identification number so that it can be tracked using barcode scanners.
- Choose a printer for your barcodes. Decide whether your barcode will carry GS1 identification keys and attributes as static or dynamic information. A barcode can be printed using traditional techniques directly onto a package or label if the information is static. For dynamic information, either a digital or a combination of digital and traditional printing will be required.
- Establish a primary scanning environment. Specifications for your barcode type, size, placement, and quality depend on where the barcode will be scanned such as the retail point of sale or in a logistics environment.
- Select a barcode. Choosing the right barcode is vital to the success of your barcode inventory system implementation plan. Factors to consider will depend largely on your scanning environment.
- Pick the correct barcode size and symbol. The information and size of a barcode symbol depend on the symbol specified, where it will be used, and how it will be printed. Each scanning environment lists relevant symbols with their target X-dimension and the matching target height. A major consideration for barcode symbol size is the capability of the selected printing process.
- Determine barcode text. The text below a barcode, called Human Readable Interpretation is a backup for if the barcode is poor quality or damaged. It must be legible, proportional, and grouped below the barcode.
- Choose your barcode colour. The best colour for a barcode is black bars on a white background. While other colours can be used, they must be dark for bars and light or reddish for backgrounds and spaces. The bars must be of a single colour and not printed by multiple tools.
- Pick the barcode placement. Barcode placement refers to the symbol location or placement on the design. When you’re assigning barcode symbol placement, consider the packaging process. Once the proper placement is determined, consult with the printing company – many printing processes require barcodes to be printed in a specific orientation to optimise printing processes.
- Build a barcode quality plan. To do this, you can use the ISO/IEC 15416 Barcode Print Quality Test Specifications for linear symbols and ISO/IEC 15415 Barcode Print Quality Test Specifications for 2D Symbols. To set up different minimum specifications, you can use a standardised test and the GS1 General Specifications. The GS1 General Specifications is the core standards document of the GS1 system that describes how GS1 barcodes and identification keys should be used.
These steps provide a general guideline for setting up a barcode inventory system in your business. However, there are additional steps you may be required to take depending on your business model and inventory requirements.
Up next we'll cover how barcode inventory systems can be implemented in a factory, a warehouse, or a small retail business.
How to set up a barcode system in manufacturing
Traceability is essential in the manufacturing industry. There are numerous traceability benefits for manufacturers who invest in an effective barcode inventory system.
A barcode system in manufacturing can enable:
- More streamlined quality control processes
- Better management of regulatory compliance
- Easily handle recalls and return merchandise authorisations
- Improve your overall level of inventory control and supply chain
One way to set up a barcode system in manufacturing is to implement batch tracking for your products. Batch tracking enables end-to-end traceability and is achieved by implementing a barcode system where you can assign a unique batch number to each batch of finished goods.
This method makes it easier to track defective products or goods approaching their expiry date. You can track and monitor relevant information on product batches such as the suppliers of raw materials or manufacturing dates and locations.
To track batches with barcodes, use batch-tracking software that integrates (or comes included) with your inventory management system. This will allow you to track the movement of each batch through the manufacturing process.
How to set up a barcode system in a warehouse
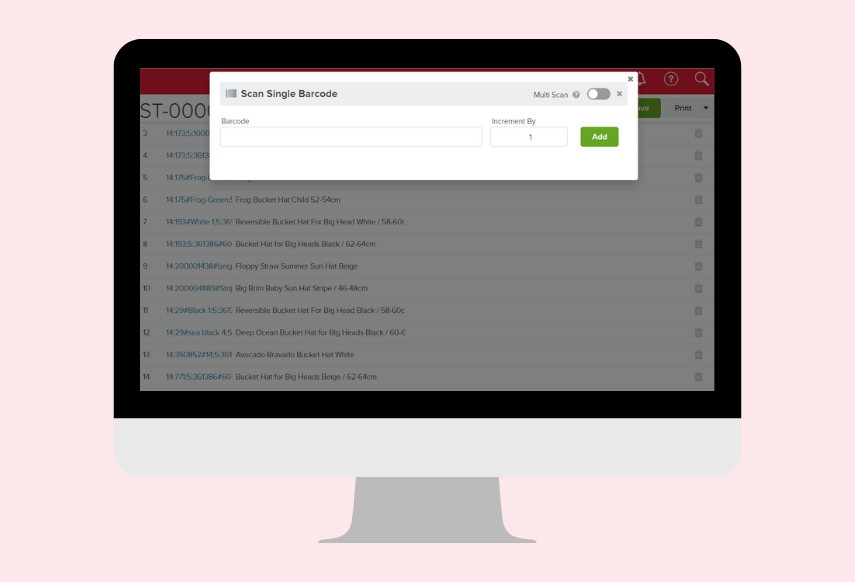 An example of how a barcode inventory system can be used to facilitate faster warehouse stocktaking.
An example of how a barcode inventory system can be used to facilitate faster warehouse stocktaking.
Setting up a barcode system in your warehouse allows you to effectively monitor your warehouse capabilities in real time.
Barcoding improves warehouse operations by maximising the efficiency and productivity of receipt and dispatch functions. Staff can quickly and effortlessly confirm that stock meets order requirements through the simple act of scanning barcodes.
Follow these steps to set up a barcode system in your warehouse:
- Prepare your inventory for barcoding by eliminating clutter and ensuring inventory is stored in the right locations. Storing stock in the right spot expedites the picking process and will make your stocktaking processes quicker and easier.
- Assign a unique barcode to each product and to the location where it will be stored.
- Start entering inventory items and SKU details into your software’s digital inventory list.
- Print the barcode onto labels with other details, such as the name of the SKU or your logo.
- Label everything with barcodes using the barcode generator in your inventory system.
Once a barcode inventory system has been set up in the warehouse, staff will be able to scan individual items and then the corresponding bin number. The barcode system will verify that goods have been placed in the correct location.
Pro tip: Your stock with the highest inventory turnover should be placed in easy-to-access locations closest to dispatch to improve your fill rates and overall inventory control.
How to set up a barcode system for small business
A barcode inventory system for small businesses needs to have a good mix of hardware (to scan and print labels) and software (to act on each scan).
The first step in implementing a barcode system for your small business is to choose the right inventory management software – one that has a built-in barcode and QR code scanner. Then follow the steps below to set it up:
- Ascertain industry barcode standards. You might want to use SKU barcodes for your own inventory management, but the goods you sell carry these barcodes. If you are selling B2B the barcode you choose must comply with industry standards and barcode usage guidelines.
- Define the barcode functions. Inventory applies to a wide range of assets, such as goods you produce, products you’ve purchased for resale, and items you bought to use. Your inventory function categories may also include packaging materials, maintenance, repair, and operating supplies.
- Decide the barcode information to be stored in your barcode. This includes features such as the item’s name, description, product category and variations such as colour or size. The amount of information you want to encode will dictate which barcode to use, depending on any industry guidelines.
- Select your barcode hardware and software. Barcode scanners come in a range of shapes, sizes, and price points; small businesses can even turn smartphones into barcode scanners. However, you need to make sure your barcode software integrates with your POS and/or accounting software.
- Implement barcode inventory procedures. Use standardised processes to ensure data accuracy. Train your staff on how to use the inventory barcode system effectively.
Barcode inventory system best practices
Whether you’re setting up a barcode system for a small business or implementing a barcode system in a warehouse, there are steps you can follow to make the most of it. Here are our top picks.
6 actionable barcode inventory system best practices:
- Implement a comprehensive inventory management system to track and monitor inventory levels.
- Synchronize the barcode system with the inventory management software to get real-time updates on inventory counts and other relevant data.
- Use the highest-quality inventory barcodes and integrate your barcode inventory system with other software such as your accounting, shipping, and POS systems.
- Implement automation for efficient barcode inventory control with barcode scanners that read the barcode, sending the information to your inventory management software in real time.
- Train your staff on how to use the barcode inventory system effectively. Educate employees and ensure you have their active participation so that the entire team is producing consistent, accurate results.
Once you've implemented and begun to use a barcode inventory system, it's a good idea to establish inventory KPIs to measure performance. Consider tracking key metrics such as managing safety stock levels, stock-to-sales ratios, sell-through rates, and other inventory ratios to help reduce the cash you have tied up in your inventory.
More posts like this:
