
Order management systems are software applications that automate your various order management processes. They enable you to manage your inventory, sales, and customer information in one place – saving time and making the business more efficient.
In this article, we’ll look at how an order management system works, the types of order management systems for different sectors, and look at some of the challenges of implementation.
What is an order management system?
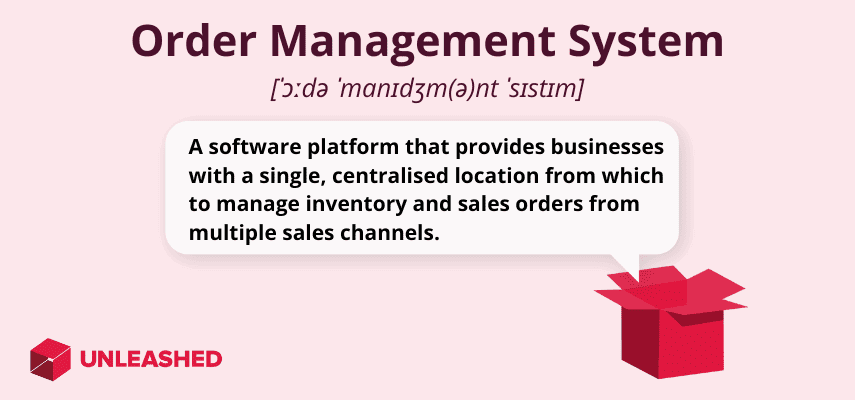
An order management system (OMS) is a software platform that helps businesses manage sales, order processing, inventory, and fulfilment. The software is designed to streamline your entire order management process through the automation of tasks and the provision of real-time visibility into your inventory levels and customer order status.
What does an order management system do?
An order management system provides businesses with a single, centralised platform to manage orders from multiple sales channels, including brick-and-mortar retail, websites, eCommerce stores, mobile Apps, and kiosks.
Order management systems simplify the purchase process for customers and make it easier for businesses to manage orders, inventory, fulfilment, and returns. They help you fulfil orders faster by automating previously manual tasks from your purchasing and fulfilment processes for you and your customer.
How order management systems work
An order management system helps businesses to manage their order-processing workflow. Here’s a brief overview of how an order management system works.
1. Order receipt
The order receipt stage is the first step of the order management lifecycle.
Customers place orders through various channels, such as email, phone, or a website. The OMS captures the order information and verifies it for accuracy. The customer order details are then recorded in the order management system.
This initial received stage is critical to the success of the order management process because it sets the foundation for the subsequent stages of the lifecycle.
2. Order processing
Processing is your order fulfilment stage. It involves processing the order, picking the items from the inventory, packing them ready for shipping, and dispatching them to the customer.
The OMS sends the order information to the warehouse or distribution centre, where the order is picked, packed, and labelled. It then tracks the order status and updates the customer on its progress.
Managing the processed stage of orders involves ensuring that orders are properly prepared and delivered to the right place.
An automated order management system can help businesses improve accuracy and decrease the time it takes to fulfil orders. A cloud-based OMS updates your inventory levels in real time as orders are processed.
3. Order reconciliation
The reconciled stage in the order management process refers to the reconciliation of inventory levels after an order has been fulfilled. This step in the order management process ensures that the inventory levels are accurate and up to date.
The OMS reconciles the order with the accounting department, where it is recorded in the accounts receivable ledger and a receipt is sent to the customer. It also monitors stock availability and will reconcile the inventory stock to ensure levels are updated and accurate.
4. Order shipment
Finally, the order management system sends the order to the shipping carrier, which delivers the package to the customer’s address. The system tracks the delivery status and updates the customer on every stage of its progress.
Order shipment also refers to the after-sales activities that occur once an order has been shipped, such as the returns handling process, refunds, and exchanges.
Some after-sales processes of an order management system include:
- Customer feedback is used to improve the quality of the product or service.
- Efficient handling of returns and refunds when the customer is unsatisfied with a product.
- Processing warranty claims for faulty items.
- Providing customers with after-sales product support.
These after-sales processes help businesses maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty and are an essential part of any order management system.
Benefits of an order management system
Efficient order management is critical for any business, regardless of its size. It comprises the activities of receiving, tracking, and fulfilling customer orders.
The main benefits of an order management system are that it helps businesses streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction levels.
Additional benefits of an order management system include:
- Efficient order processing: An order management system can help automate the order processing and fulfilment process. It helps to reduce errors in your order fulfilment processes, helping save time and money.
- Improved inventory management: An OMS keeps track of your inventory levels in real time, helping you avoid stockouts, reduce overstocking, and optimise your inventory levels.
- Greater efficiency: By automating the order management process, you can increase your efficiency and productivity. This can help them save time and money, allowing them to focus on growing their business and serving their customers better.
We recently asked Bernadette Newman, Operations Manager at Atlas Flowers – a business-to-business ecommerce wholesaler – about the benefits of using the Unleashed order management system. She told us:
“Tracking product sale performance within Unleashed assists with stock procurement. Buying patterns develop over time and predictions can be made as to what needs to be purchased, how much, and when. Identifying slower-moving items can guide marketing activities to clear stock.”
 Order management systems can help small businesses deal with a large volume of sales orders faster.
Order management systems can help small businesses deal with a large volume of sales orders faster.
Key order management system features
If you’re in the market for an order management system, you should make a list of the functionalities that will be the most useful for your operations.
Some key order management system features to consider:
- Multichannel sales: An effective OMS supports multi-integration with various sales channels, including online marketplaces, social media platforms, warehouses, and your brick-and-mortar stores. This allows for cross-platform reporting and ensures sales and inventory data is accurate and updated across the business.
- Cloud-based order management: An OMS that stores data in the cloud can reduce errors and delays in order processing. This is achieved through automated order processing, real-time inventory tracking, and order validation.
- Inventory optimisation: Tracking inventory levels and comparing historical performance data with current market trends enables businesses to optimise stock levels, reduce overstocking, and prevent stockouts.
- End-to-end order fulfilment: Manage your entire order fulfilment process in one location, from order entry to shipping and delivery. A good order management system will provide real-time tracking of shipments and delivery status.
- Analytics and reporting: Real-time insights into order processing, inventory levels, and customer behaviour can help you make data-driven decisions that optimise your order management capabilities.
When choosing an OMS for your business, it’s important to consider factors such as scalability, integration with other systems, and ease of use.
Order management system types and examples
The primary purpose of an OMS is to provide a centralised system for managing orders, inventory, and customer data. An OMS allows businesses to monitor and track orders in real-time, from the point of sale through to delivery – making it quicker for you to identify and resolve any issues and manufacturing bottlenecks that may arise during the process.
An OMS can be particularly useful for businesses with a multichannel sales strategy, a high volume of orders, or that operate in complex supply chains. It’s important to note that the order management process will vary depending on your business and industry.
eCommerce order management system
An eCommerce order management system automates the order fulfilment process, handles reverse logistics, manages customer information, and merges order and financial data.
Shopify is an example of an eCommerce order management system. It’s an eCommerce platform that helps businesses manage their order processing workflow through their website, and from other eCommerce sales channels.
While Shopify may be sufficient for managing a low volume of orders, businesses often outgrow the platform’s capabilities. When this happens, an order management system that integrates with Shopify may be implemented to support future growth and improved efficiency.
 A key benefit of order management systems is that they allow you to compare sales data between different channels.
A key benefit of order management systems is that they allow you to compare sales data between different channels.
B2B order management system
A business-to-business (B2B) order management system helps B2B businesses manage their sales and inventory.
OMS is important for B2B because it helps organisations manage their orders and inventory more efficiently, improve customer experience, and increase profitability. It can also help you to provide a better customer experience by reducing the time it takes to fulfil orders and ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time.
Some B2B eCommerce platforms, such as the Unleashed B2B store, also enable you to set unique pricing for each of your customers. And because it can be accessed without an intermediary (such as a salesperson), you can continue to make sales out of hours.
When choosing an OMS for B2B, look for a system with order confirmation features or the capability to send automatic confirmations to customers after a purchase.
Order management system for manufacturing
An order management system for manufacturing helps to connect inventory management and sales with production. Direct-to-consumer (D2C) manufacturers looking to improve manufacturing and sales order management, stock control, and production planning should look for a reliable manufacturing order management system.
A manufacturing OMS is specifically tailored and designed to manage the unique requirements of manufacturing orders, with features that include a bill of materials and quality control management not typically found in other order management systems.
Order management system for small business
Small businesses often start by managing their orders manually.
Previously this involved using time-consuming paper-based systems to record and track orders, invoices, and receipts. Small business owners might use a combination of filing cabinets, ledgers, and index cards to keep track of their orders, and manual methods to calculate inventory levels and reorder points.
Unfortunately, these types of systems are typically error-prone and unsustainable. The process is labour-intensive and requires a lot of manual effort. With the advent of computers, small businesses started imputing this information into spreadsheets that still require manual updating and are prone to human error.
Small businesses can benefit significantly from implementing an order management system. You can use this software to automate order management processes, making it easier to manage orders, track inventory levels, and generate invoices and receipts.
Order management system demo
Check out this short demo to see how order management systems can help improve your processes:
Order management system implementation challenges
As with any software implementation, there are risks and challenges involved with setting up an OMS for your business. It’s important to be across these before you invest in a new tool so that you’re prepared to tackle anything that comes up during implementation.
Challenges of implementing order management systems include:
- Data gaps and inconsistencies that lead to fulfilment errors, order cancellations, and poor customer experience.
- Integration inefficiencies that result in communication problems, inventory mismatches, and shipping mistakes.
- Insufficient or redundant features that complicate the order management process and that unnecessarily cost the business money.
- Lack of scalability and flexibility limiting the growth potential and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Poor customer service and support that damage your brand reputation and customer loyalty.
In addition to these, it pays dividends to get your whole team on board right from the start – from executives and stakeholders down to the warehouse staff that will be using the new system every day.
Order management system implementation best practices
To help you manage some of the challenges we just mentioned, here are some order management system best practices for getting started on the right foot.
1. Identify your business procedures, work process, objectives, and targets
Before implementing an order management system, it’s essential to understand your business’s unique requirements, such as the number of orders you receive, the channels you sell through, and the types of products you offer.
2. Assess the advantages and costs of implementation
Implementing an order management system can be a significant investment in terms of time, money, and resources. It’s essential to evaluate the benefits and costs of implementing the system, such as increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved customer experience, against the investment required.
3. Plan accordingly
Once you’ve decided to implement an order management system, it’s crucial to plan the implementation process carefully. This includes setting realistic timelines, identifying key stakeholders, and allocating resources such as personnel, hardware, and software.
4. Document the process
Documenting the implementation process is essential for ensuring that everyone involved in the process understands their roles and responsibilities. It also helps to identify any gaps or inefficiencies in the process that need to be addressed.
5. Train your employees
Training your employees on how to use the order management system is critical for ensuring that the system is used correctly and efficiently. This includes providing training on how to enter orders, track inventory, generate invoices and receipts, and manage customer data.
6. Test the system
Before going live with the order management system, it’s essential to test the system thoroughly. Test the OMS’s functionality, performance, and security to identify any issues or bugs that may affect its performance.
7. Monitor and evaluate the system
Once the order management system is live, it’s essential to monitor and evaluate its performance regularly. This includes tracking key performance indicators such as order processing time, inventory accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
