How to Improve Productivity and Efficiency in Manufacturing
Improving productivity and efficiency in manufacturing is the secret to steadier cash flow, stronger profit margins, and increased customer satisfaction.
Long story short: the more productive you are, the more competitive you are.
When improvement becomes an ongoing focus, your business will see happier staff, shorter production lead times, and simplified workflows – on top of the long-term financial gains.
This guide will show you how to improve productivity and efficiency in manufacturing, reduce your company’s production costs, and be more efficient in your daily operations.
In this guide
- What is manufacturing productivity?
- What is manufacturing efficiency?
- What is production efficiency, and how does it differ from operational efficiency?
- Manufacturing efficiency vs. manufacturing productivity
- Essential manufacturing efficiency metrics and formulas
- 5 proven steps to improve manufacturing efficiency
- Improve manufacturing efficiency with cloud software
What is Manufacturing Productivity?

Manufacturing productivity is a performance metric that measures the rate at which a specific volume of goods is produced by a company. It evaluated how effectively your manufacturing operation converts time, labour, and resources into finished products.
Manufacturing productivity can be improved by:
- Increasing employee productivity
- Eliminate factory waste
- Boost operational efficiency
- Integrate your supply chain
- Reduce production costs
The higher your manufacturing productivity, the faster you’ll meet customer demand, reduce lead times and improve profitability – while maintaining consistent product quality.
How to Improve Manufacturing Productivity?
1. Increase employee productivity
Improving the productivity of your employees directly lifts the performance of your business. Consider how staff can work more efficiently on their assigned tasks. Once, that simply meant forcing people to work faster. But this approach isn’t sustainable.
A more modern strategy is to find healthy ways of motivating your employees to excel at their jobs.
Another approach is to step back and ask which tasks your people can add the most value to.
That doesn’t mean replacing workers with machines, but rather looking for ways you can automate non-value-adding tasks, like data entry or counting stock, so that your staff are freed up for more value-adding work.
2. Improve manufacturing productivity by reducing waste
In a manufacturing business, waste strains profitability.
Manufacturing waste can come in the form of time, resources, and labour. It shows up through insufficient process planning, inventory imbalance, or poor warehouse layout.
Essentially, waste is any expense or effort that does not efficiently transform raw materials into a finished product. By streamlining your production processes and eliminating wasteful expenditure, you can add new value to each phase of production.
3. Establish more efficient manufacturing operations
Operational efficiency is about delivering good-quality products to the right customers in the most cost-effective and timely manner. As a result, it directly contributes to manufacturing productivity.
There are four factors that contribute to operational efficiency:
- Resource utilisation
- Production efficiency
- Distribution methods
- Inventory management
By focusing your efforts on each of these key areas, you can begin to establish optimised workflows that contribute to greater business performance and higher output – the cornerstones of ideal manufacturing productivity.
4. Optimise your supply chain
Not all manufacturing productivity gains are achieved internally; sometimes you need outside help.
Supply chain management is an often-ignored strategy for improving manufacturing productivity.
But if you manage your supply chain well, you can get the best rates and products in the shortest possible time. In turn, this reduces your total inventory costs and improves your production efficiency.
Additional benefits of effective supply chain management also include healthier supplier relationships and better supply chain visibility, ultimately facilitating smarter and more cost-effective production planning.
5. Minimise production costs
Another way to improve manufacturing productivity is to reduce your total production costs.
Production costs are the costs incurred in manufacturing a product or providing a service. These can include expenses such as raw materials, labour, suppliers, and general overhead – as well as any government taxes and royalties.
Improved profitability is the obvious benefit of fewer production costs. But reducing these costs also frees up capital that can then be invested in efficiency-boosting resources, such as more effective tools, more staff, or better manufacturing software.
What is Manufacturing Efficiency?
Manufacturing efficiency is a performance measurement that reflects how effectively a manufacturing process converts inputs – such as raw materials, labour, and energy – into outputs (finished products). Measuring efficiency helps you understand how productively your factory or production line operates and identify any opportunities for process improvement.
Let’s look at a quick example.
Imagine two factories manufacturing the same type of product. In the same amount of time and with the same resources, one factory produces twice as many products. That factory is more efficient because it's achieving more output with fewer inputs.
Efficiency in manufacturing can be improved in several ways, including:
- Optimising production processes
- Reducing waste
- Improving equipment reliability
- Enhancing workforce skills
- Utilising technology effectively
Ultimately, the better your manufacturing efficiency, the more opportunity you’ll have to lower production costs, realise higher productivity, and achieve greater competitiveness in the market.
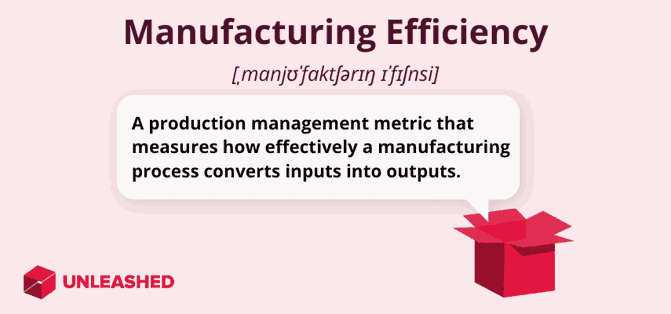
What is good manufacturing efficiency?
Good manufacturing efficiency refers to the ability of a manufacturing operation to consistently produce high-quality products at optimal levels of productivity while minimising waste and resource consumption. It can be defined as achieving the desired output with the least amount of input – whether that's fewer raw materials, labour, time, or energy.
A manufacturing process with good efficiency operates smoothly, with minimal downtime and disruptions, while effectively utilising available resources – such as machinery and labour – to maintain product quality and meet customer demands.
Key indicators of good manufacturing efficiency include:
- High production rates
- Low defect rates
- Minimal downtime
- Economical use of materials and energy
- Streamlined workflows
- Satisfied customers

Lift your manufacturing productivity today
What is Production Efficiency and How Does It Differ from Operational Efficiency?
Production efficiency focuses on converting inputs into outputs with minimal waste. Operational efficiency, however, looks at the entire operation – workflows, resource allocation, and cost-effectiveness.
Think of production efficiency as “doing things right” and operational efficiency as “doing the right things in the best way”. Both are essential for reducing downtime and improving throughput.
Manufacturing Efficiency vs. Manufacturing Productivity
Manufacturing efficiency and manufacturing productivity are closely related, but they measure different aspects of the manufacturing process. Manufacturing efficiency focuses on optimising the use of resources within the production process, while manufacturing productivity measures the overall output generated relative to the resources expended.
Let’s break down these differences.
Manufacturing efficiency centres on how well resources are utilised to produce a given output. It measures the effectiveness of the production process in minimising waste, reducing costs, and maximising output with the available resources. Efficiency focuses on improving metrics like machine uptime, cycle time, defect rates, and utilisation of labour and equipment.
On the other hand, manufacturing productivity measures the output generated from a given input of resources. It quantifies the relationship between the amount of goods produced (output) and the resources used to produce them (inputs) – such as labour, capital, and materials. Productivity metrics may include units produced per hour, revenue per employee, or output per unit of input.
Essential Manufacturing Efficiency Metrics and Formulas
To measure efficiency in a manufacturing business, you must first acquire evidence of your production output, total manufacturing costs, and any other information pertaining to resources used in the production process. This data can be worked out manually, or (if you’re already using cloud manufacturing software) you can access it with your system’s analytics tools.
Manufacturing Efficiency Formula
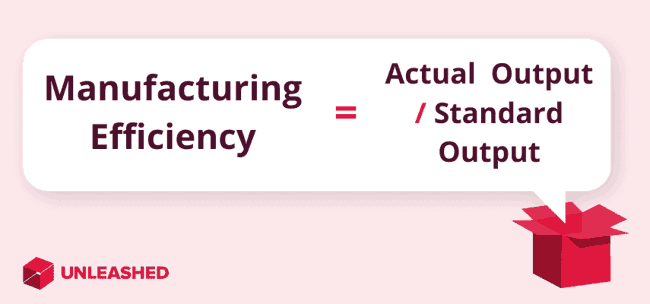
The manufacturing efficiency formula is a calculation used to assess how efficiently a manufacturing process is converting inputs into outputs. In essence, it compares the actual output achieved with the maximum potential output that could be achieved under ideal conditions.
Here's the manufacturing efficiency formula:
Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency
Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency (MCE) measures how much of the total production time is spent on value-added activities – converting raw materials into finished products – versus non-value-added time, or waste. A higher MCE indicates that a greater proportion of your cycle time is productive, meaning higher efficiency.
Here’s the manufacturing cycle efficiency formula:
MCE (%) = Value-Added Time / Total Cycle Time
For example, if value-added time = 20 hours and total cycle time = 50 hours:
MCE = 20 ÷ 50 = 0.4 (or 40%)
Other useful manufacturing efficiency metrics
There are some more useful manufacturing efficiency metrics to help you assess various aspects of a manufacturing operation beyond output quantity. These provide insights into different aspects of production, quality, and resource utilisation.
Other handy metrics for measuring manufacturing efficiency:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): OEE measures the overall performance of equipment in terms of availability, performance efficiency, and quality rate. It helps identify equipment downtime, speed losses, and defects – providing valuable insights into equipment effectiveness and potential improvements.
- First Pass Yield (FPY): FPY calculates the percentage of products that pass quality inspections without requiring rework or repair during the initial manufacturing process. It helps gauge the effectiveness of quality control measures and identify areas for improvement in production processes.
- Throughput: Throughput measures the rate at which a manufacturing process can produce output over a specific period. It indicates production capacity and helps identify production bottlenecks that may limit overall throughput.
- Inventory turnover ratio: The inventory turnover ratio measures how quickly inventory is being converted into sales. It helps assess inventory management efficiency and identify excess inventory levels or slow-moving inventory that may be tying up capital.
- Lead time: Lead time is the time it takes for a product to move through the entire manufacturing process, from order placement to delivery. It helps identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the production process and ensures timely delivery to customers.
- Supplier performance metrics: These metrics evaluate the performance of suppliers in terms of quality, delivery time, and cost. By monitoring supplier performance, manufacturers can ensure a reliable supply chain and minimise disruptions to production.
- Employee efficiency metrics: These metrics assess the productivity and performance of employees, such as labour utilisation, absenteeism rates, and training effectiveness. They help identify opportunities for workforce optimisation and skill development.
By tracking these additional manufacturing efficiency metrics, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of production operations and identify key areas for improvement.
5 Proven Steps to Improve Manufacturing Efficiency
1. Analyse Takt Time
Calculate Takt Time to align production speed with customer demand. This ensures balanced workloads and prevents bottlenecks.
Formula:
Takt Time = Available Production Time / Customer Demand
By understanding Takt Time, you can synchronise production with demand, reduce idle time, and improve flow across your manufacturing process.
2. Tighten Up Your Processes
Identify and eliminate unnecessary steps, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies in production workflows to optimise the manufacturing process.
- Map out workflows to spot delays and redundancies.
- Standardise procedures to reduce variability.
- Use data-driven analysis to prioritise improvements.
3. Invest in Technology and Automation
Adopt advanced manufacturing technologies such as automation, robotics, and digital manufacturing tools to:
- Enhance productivity and reduce manual labour.
- Improve process control and consistency.
- Increase throughput and minimise downtime.
4. Implement Lean Manufacturing Principles
Lean principles – such as continuous improvement, waste reduction, and value stream mapping – help eliminate non-value-added activities.
Focus on reducing the seven types of waste: overproduction, inventory, motion, defects, overprocessing, waiting, and transport.
5. Optimise Supply Chain Management
Strengthen collaboration with suppliers, improve logistics, and implement just-in-time inventory practices to:
- Minimise inventory holding costs.
- Reduce lead times.
- Ensure a reliable supply of materials for smooth production operations.
Improve Manufacturing Efficiency with Cloud Software
Unleashed inventory management software provides real-time visibility across production processes, inventory, and costs. This helps identify inefficiencies and optimise workflows.
Start your 14-day free trial to improve your manufacturing efficiency with inventory management software.















