
Stock control is a necessity for every business that deals in physical goods. Done well, stock control maximises profits and builds customer loyalty; done badly, it can lead to business failure.
Here are the basic elements of good stock control, including definitions, methods and tools used.
What is stock control?
Stock control, also known as inventory control, is keeping all the different products in a business within ideal minimum and maximum levels, so the business can fulfil orders without delay, while keeping stock holding costs to a minimum.
In short, effective stock control maintains a balance between meeting customer demand and controlling inventory expenditure and risk.
Overstocking is one of the main risks of poor stock control that business try to avoid. The immediate impact of overstocking is the capital outlay required to buy the stock. While this money is still in the business when stock is purchased – and in principle ought to turn into profit when those goods are sold – buying stock locks cash up in physical goods, meaning it can't be spent on other parts of the business.
Buying stock also introduces an element of financial risk.
Stock that is purchased but doesn't sell can become waste – whether by expiring, becoming unsaleable, or from being damaged – and storing stock costs money: 3PL warehouses charge by volume, so carrying more stock than is needed to meet demand represents an ongoing drain on finances.
Ultimately stock control can be the difference between loss and profit. Done right, it keeps costs down while increasing profitability on every sale.
Stock control methods
The different stock control methods you employ in your business will help you build an efficient system for tracking stock through the supply chain.
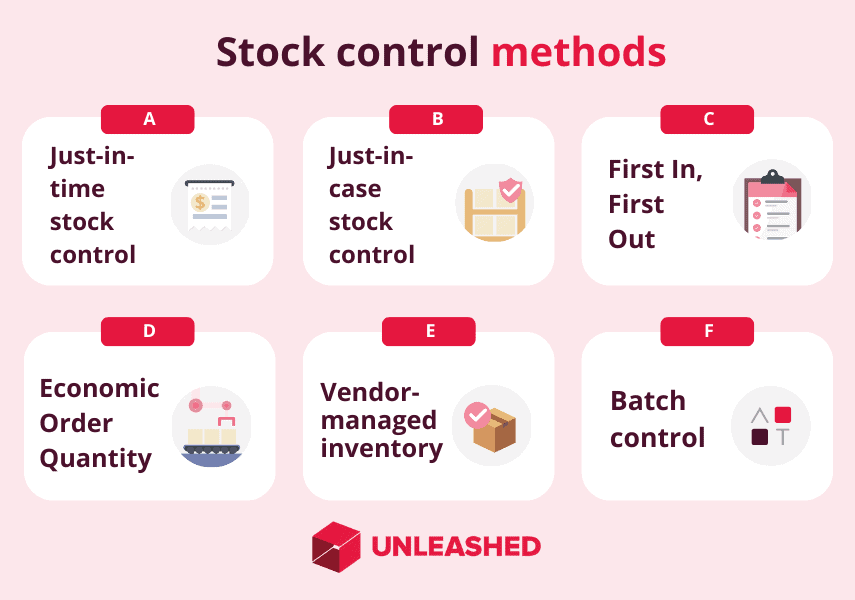
Popular stock control methods include:
- Just-in-time (JIT) stock control
- Just-in-case stock control
- FIFO (First-In, First-Out)
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
- Vendor-managed inventory
- Batch control
#1 Just-in-time stock control
The just-in-time stock control method focuses on maintaining the minimum stock level for each of your stock items. By minimising how much stock you carry in the warehouse at any one time, you're able to mitigate the risks and costs of holding too much inventory.
#2 Just-in-case stock control
The JIC stock control method functions as a safety net against stockouts. It involves carrying extra a few stock items as a safety buffer for each stock-keeping unit, in case of supply chain disruptions or other inventory challenges.
While this strategy is helpful for improving the customer experience, it comes with a risk of tying up your capital in excess inventory. To ensure efficient stock control using this method, you must have accurate inventory forecasting.
#3 FIFO
FIFO is an effective stock valuation method for tracking the value of your inventory. Goods that are purchased or manufactured from raw materials first are the first to be sold to customers. In this way, you can easily assign the correct value when determining your cost of goods sold (COGS).
#4 Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The EOQ formula calculates your ideal quantity of goods when placing purchase orders with your suppliers. It compares the cost of holding and selling goods with your annual demand to determine optimal stock levels and optimal reorder frequencies.
#5 Vendor-managed inventory
Vendor managed inventory leaves the responsibility of controlling stock with the supplier. This stock control method requires little or no stock planning on the retailer's end, as it is based on an agreement that the company providing the goods shall incorporate stock tracking and management into their relationship.
#6 Batch control
The batch control approach involves controlling stock using identifying characters such as batch numbers, lot numbers, production dates, and serial numbers – rather than individual stock-keeping units (SKUs). This method enables businesses to track and make decisions on large groups of inventory at one time.
Regardless of which stock control method you use, you need to have a stock control system in place.
Stock control systems
A stock control system, also known as an inventory control system, incorporates all the functions are associated with inventory management and maintenance. It should encompass everything from purchasing, product tracking, and product turnover to storage inputs, shipping and receiving and re-ordering products.
There are two types of stock control system: manual and automated.
The most basic, manual system is writing it down in a stock book, on a stock card or using spreadsheets. While this works for a business just starting out, it cannot be sustained as a business grows.
For that, you need an automated stock control system.
Features of an automated stock control system
An automated stock control system helps businesses maintain a competitive edge and maximises productivity.
Common features of an automated stock control system:
- Real-time, perpetual inventory tracking. This means keeping track of inventory as it moves; you don't want to run your business using outdated stock figures as it can harm your supply chain.
- Support for sales and shipping. You'll want a system that can generate fulfilment documentation such as picking and packing notes, and invoices.
- Support for procurement. Features such as automated reordering and supplier price lists reduce friction in the purchasing process.
- Integration with other programs. If you're looking for maximum efficiency and accuracy, make sure your chosen system integrates with your CRM, ERP, accounting or other management systems.
- Generate useful reports. Important types of inventory reports include inventory summaries and totals, transaction reports and order history.
You'll find many of these features (and more) in cloud-based stock management software.
Stock control software
Now that you know what to look out for in your inventory control system, you need to decide what stock control software works best for your business.
Effective stock control can be achieved by choosing a system with the features you need most.
Talk to the relevant people in your business, then come up with a checklist of features you want.
Useful stock control software features include:
- Ability to use multiple currencies
- Ability to cover multiple warehouses
- Can adapt to your business as it grows
- Serial/Batch tracking
-
Support multiple users at once
Growing businesses should look to cloud software for effective inventory management. There are many benefits to having your business in the cloud.
Businesses that have scaled their business efficiently with cloud-based software include:
- Traders Warehouse, a UK-based electronic security equipment distributor
- Montana Colors AU, the leading supplier of graffiti art products in Australia
- Good Buzz, kombucha maker and retailer based in New Zealand
- La Tortilleria, makers and suppliers of authentic Mexican corn tortillas, tortilla chips in Australia
- Seven Bro7hers Brewery, UK-based brewery run by seven brothers who all share a passion for beer
Benefits of cloud-based stock control software
Cloud-based stock control software enables you to ditch your manual stock control methods for an automated approach to inventory management that brings costs down and efficiency up.
Key benefits of cloud-based stock management software include:
- More effective stock management. The inventory, sales, and purchasing decisions you make for your business can be inspired by accurate, real-time data about your business.
- Instant stock valuation when you need it. Because data is updated across the business via the cloud, you'll be able to see exactly how much stock you have – and it's total value – whenever you need to know.
- Improved stock quality control. When your stock management process isn't automated, it's easy to let poor quality slip through the cracks. Cloud software systems ensure every important inventory management procedure happens the way it should.
- Streamline the production process. Some inventory management software includes functionality for assembling finished goods out of raw materials and components. Check for bill of materials features if your business manufacturers its own products.
- Prevent overstock and stockouts. Cloud-based stock systems can help you optimise your stock levels so you never carry too little or too much. This will help you reduce costs and is especially helpful for companies dealing with perishable stock.
When shopping for inventory management software, ask yourself what features matter most.
The stock ordering process
Getting the stock ordering process right is an important part of effective stock control. When reviewing your stock ordering it's recommended that you:
1. Stick to a single inventory control system
It is important to ascertain from the beginning what type of inventory system would best suit your business. The two options are periodic systems or perpetual systems, of which the latter is highly recommended for accuracy and ease of use.
2. Review current inventory
You need to determine what you have on hand and its value – including finished goods and raw materials. Look at your sales reports to identify your best sellers, which are making the most gross margin, and which items are slow-moving and old.
-
Learn more: 23 Types of Inventory You Should Know
3. Determine your ideal stock levels
Now you need to identify stock you always need and decide on what your maximum and minimum stock levels are for each item; it's also important to determine the minimum re-order level for each item.
Once you've identified the parameters, it's easier to know what you have to work with.
You'll also need to keep accurate stock records and make sure they match what you actually have on hand with a stocktake.
4. Constantly review inventory control
Ask yourself how stock management impacts the other areas of your business. Consider:
- Monitoring inventory metrics. One way to tell how well your current process is working is to look at the stock turn rate.
- Reviewing your purchasing patterns. Purchasing should be based on sales history and demand forecasting.
- Ordering less stock more frequently. This can improve liquidity without reducing sales.
- Consider the impact of marketing and promotion. Before launching a sales promotion, make sure you have enough stock to meet an increase in demand.
- Having a back-up plan if items don't sell as well as you wanted it to. Regardless of whether you return it to suppliers or donate it, make sure you know how to dispose of excess stock quickly.
- Reviewing your sales policies. Your sales team can strategically sell fast-moving items and clear slow-moving items.
- Storing your items more efficiently. Correct warehousing techniques are essential for best practice. Make picking and packing streamlined and efficient by storing slow-moving products at the back of the warehouse, and fast-moving goods close to the front where they are more readily accessible.
These are just some of the many aspects of stock control that should be considered. It is a good idea to start how you intend to carry on, that is, by implementing an inventory management software system that is expertly designed to facilitate excellent stock control.
More posts like this
- Inventory Control Chart: Definition, Uses, Examples - An inventory control chart is an immensely helpful tool for demand forecasting and inventory management. It helps businesses determine when to reorder...
- 10 Critical Supply Chain Management & Logistics Trends for 2024 - How is the logistics and supply chain management industry evolving – and what developments do you need to consider? We’ve read the market reports,...
- The Effect Of Seasonal Inventory On Inventory Control - Seasonal Challenges to Stock and Inventory Seasonal inventory is stock which is in high demand during particular times of the year, such as during Chr...
